The massive use of cutting-edge digital technologies has played an instrumental role in the success of China’s Covid-19 containment.
China was the first country impacted by Covid-19, and the first to work to keep a lid on soaring infection rates. In early 2020, the first battle was lost when the virus escaped the city of Wuhan and propagated a global pandemic. Yet the vast Chinese bureaucracy swung into action, employing a range of strategies to restrict the further spread of this highly contagious disease.
Sofya Bakhta, an analyst with China-based market research and consulting firm Daxue Consulting, explained:
“From identification of the first case in Wuhan through to recovery and return to a post-Covid-19 normality, China’s control of the virus has by and large been remarkable. As of August 2021, there had been 38 million Covid-19 cases in the United States compared to under 95,000 on the Chinese mainland. And there had been 630,000 US Covid-19 deaths, compared to under 4,700 in China.”

The intensive use of digital technologies has played an instrumental role in the success of China’s Covid-19 containment. From robots, autonomous vehicles and AI to apps, drones and facial recognition, a huge range of digital interventions have been used to strengthen China’s health system, implement public health measures and engage society. As Covid-19 continues to ravage other parts of the world, these technologies are still critical to China’s Covid-19 risk assessment and the functioning of Chinese healthcare services.

Sofya Bakhta said:
“There is no doubt that the Chinese have been ahead of the curve with their use of technology to prevent, detect and treat Covid-19. Regardless of how the virus originated, China has offered the world a glimpse of how to control and mitigate the impact of potential pandemics going forwards.”
A Massive Rollout of Robots, Drones and IoT Devices
From delivering groceries and cooking meals to sterilizing hospitals and patrolling the streets, China deployed robots in a wide range of settings to fight Covid-19 and minimize human exposure to the virus. In many Chinese hospitals, robots were also used to perform diagnoses, take samples and carry out thermal imaging. A robot named “Little Peanut” even delivered meals to people quarantined in a hotel, while a hospital in southern China used robots to deliver medicine and collect bed sheets and garbage.
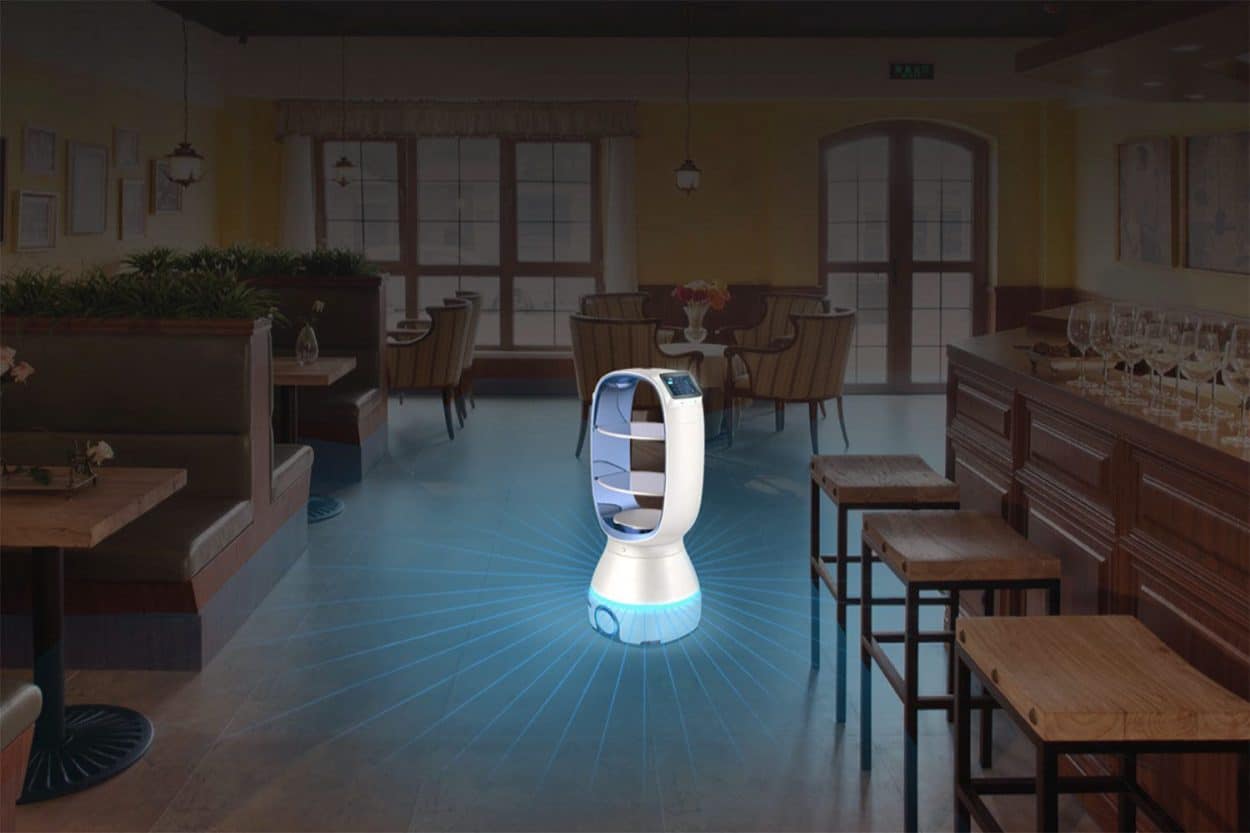

At one point in March 2020, a Wuhan-based field hospital capable of treating 20,000 patients was run entirely by AI-empowered robots and other smart IoT devices. A collaboration between Wuchang Hospital, China Mobile and a cloud robotic systems company called “Cloud Minds” saw robots orient patients, monitor vital signs, deliver food and medicine, disinfect and clean spaces and even entertain patients.
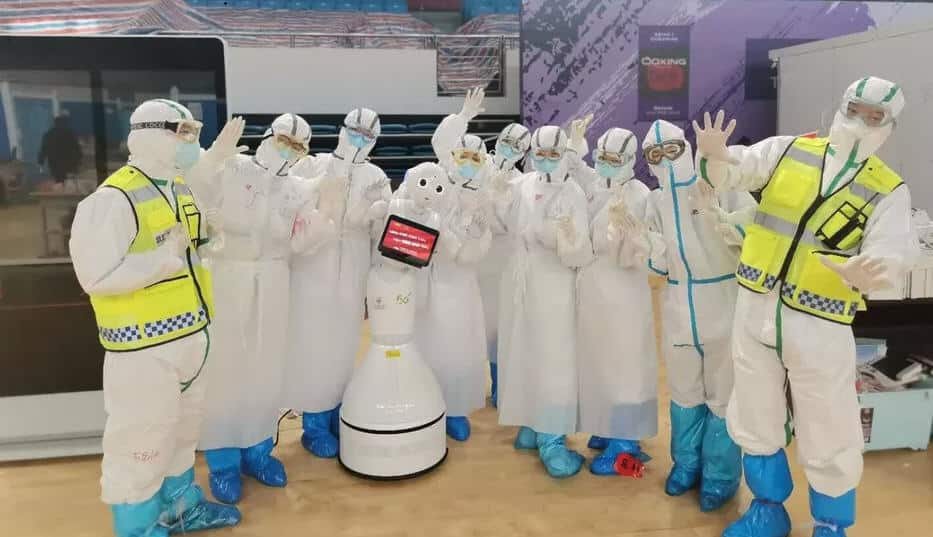
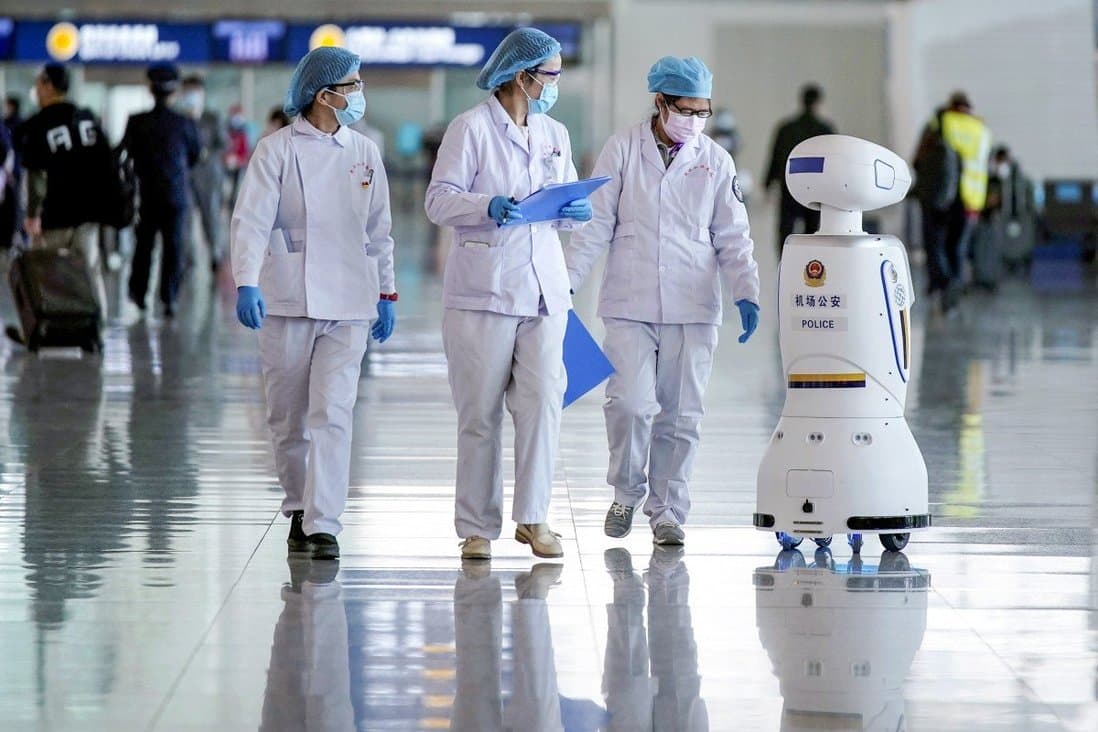


Sofya Bakhta added:
“With many Chinese hospitals working above and beyond capacity, robots helped to reduce workloads and keep patients and healthcare professionals safe. Covid-19 has really accelerated the deployment of robots in the healthcare space.”
Flying robots or drones were also widely employed to fight Covid-19, delivering biological samples and medical equipment and spraying disinfectant. Drones powered with facial recognition software were also used to broadcast warnings and tell people without masks to put them on.
Keeping Close Track
To contain Covid-19, China enabled strict policies to track the movement of citizens, quarantine high-risk cases and minimize public contact. None of these policies would have produced the desired outcome without the integrated use of advanced digital technologies.
Robert Hah, Managing Director and Strategy Lead for Accenture in Greater China, said:
“While the rest of the world struggled with a shortage of testing kits and limited hospital capacity, China leveraged location-based services (LBS) and big data analytics to identify high-risk cases, all without overwhelming the healthcare system.”
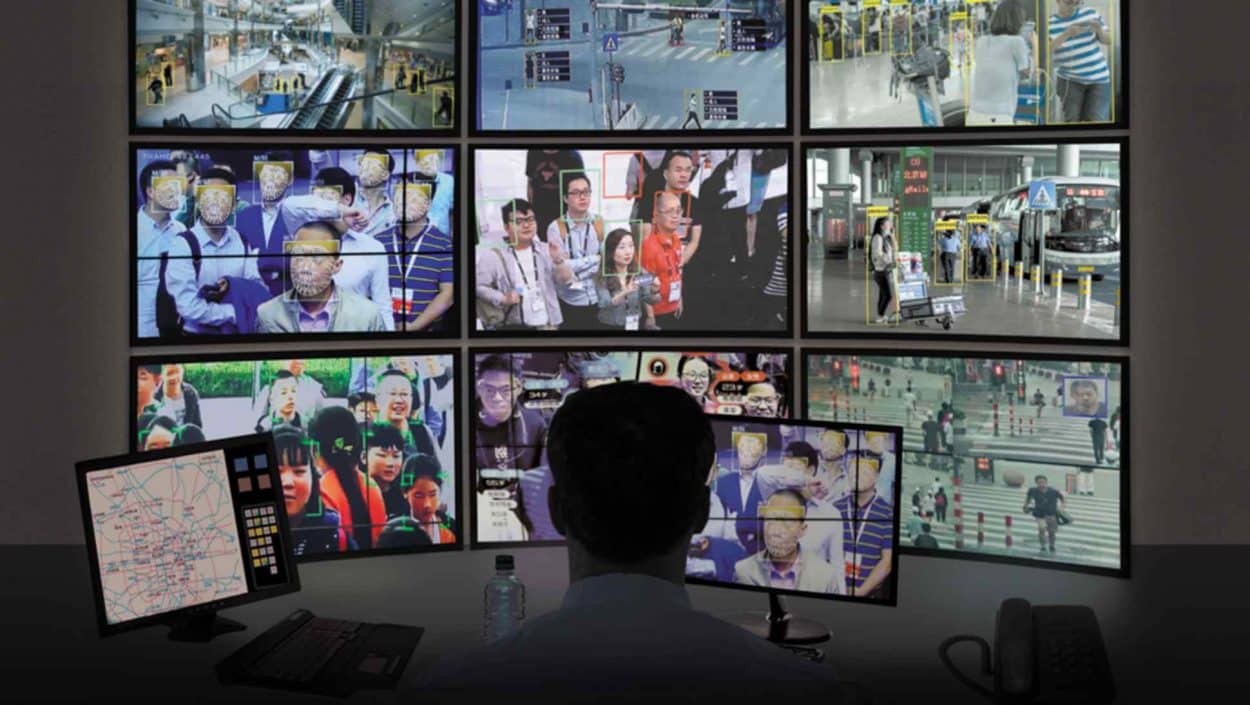

The system saw local authorities collect and aggregate the movements of all those infected with Covid-19. Coupling this with data from the national ID system, they were quickly able to identify who else may have been in close contact with them and request that they quarantine. A state-owned enterprise, the Chinese Electronic Technology Corporation (CETC) also developed a WeChat mini program that allowed citizens to self-check their risk level.
Other innovative monitoring systems included a Bluetooth-enabled tracker in Hong Kong, which was used to enforce travel restrictions for inbound travelers required to quarantine at home. These individuals were asked to wear a wristband, which was paired with their smartphone —those that left quarantine or removed the wristband were automatically reported to the authorities.
Enforcement was also ramped up on the Chinese mainland through the use of a smartphone-based, color-coded QR health code system (via Alipay and WeChat) and advanced facial recognition cameras, which controlled access to places such as transportation hubs, residential complexes and supermarkets. In Zhejiang Province alone, more than 50 million people registered for Alipay’s health codes within two weeks of release.
Robert Hah said:
“WeChat was also instrumental in keeping people updated about Covid-19. A WeChat mini-program developed by DingXiangYuan—an online community for physicians, healthcare professionals, pharmacies and facilities—used analytics to provide people with real-time insights and information about the spread of the virus.”

Designing Algorithms to Combat the Virus
Almost as soon as Covid-19 was detected, Chinese AI companies began designing or refining systems and algorithms to combat the virus. In addition to accelerating the deployment of AI-empowered chatbots connecting rural Chinese communities with healthcare professionals and machine learning algorithms for pharmaceutical research, AI was widely used to enhance public health monitoring, medical imaging, robotics and human-computer interaction.
AI was leveraged in subway stations, for example, to assist in the infrared-based temperature measurement of travelers, while Internet giant Baidu made its LinearFold algorithm available to teams fighting the virus. According to the company, the algorithm is the world’s fastest in terms of RNA structure prediction.
Sofya Bakhta said:
“I think the major takeaway in terms of AI is not the fact that China is actually using it to beat Covid, but that AI is really becoming embedded in Chinese healthcare across the board. As with robots, the pandemic has simply sped up the process.”