Recent advances from Horizon, Intuitive, and Medtronic highlight how integrated digital ecosystems are reshaping surgical precision and patient outcomes
Surgical robotics is entering a new phase of maturity defined not only by mechanical precision but also by the fusion of robotics with advanced imaging and artificial intelligence. In other words, the latest robotic platforms increasingly function as integrated digital ecosystems. Companies are working to improve robotic-assisted surgery by tackling ongoing issues like differences in patient anatomy, hard-to-reach surgical areas, and inconsistent results.
Over just the past few months, several high-profile announcements have highlighted how rapidly the field is evolving, with products pointing toward a future in which robotics not only assists surgeons but also optimizes the entire perioperative workflow to improve consistency, safety, and patient outcomes.
Polaris™ (Horizon Surgical Systems)
Horizon Surgical Systems announced this October that the world’s first cataract surgery was performed using the Polaris™ platform. The milestone procedure was completed by Uday Devgan, M.D., FACS (Fellow, American College of Surgeons), a world-renowned cataract surgeon based in Los Angeles.
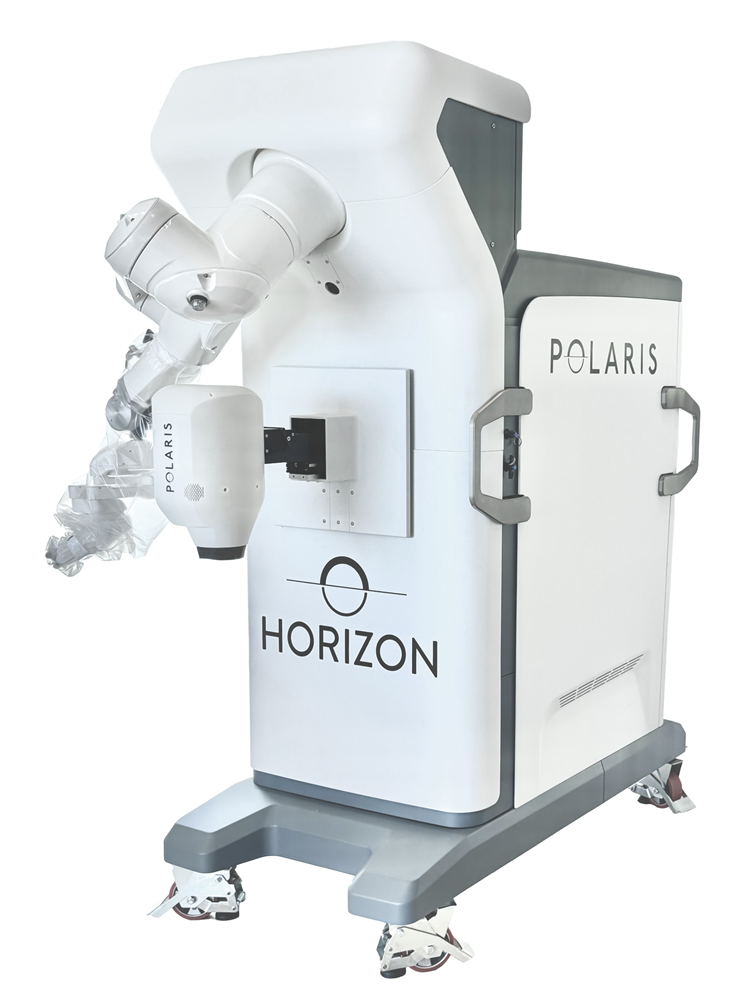

Polaris™ is the first surgical platform purpose-built for ophthalmology that fuses AI-driven visualization with micro-robotic control, aiming to reduce variability, increase precision, and integrate seamlessly into established operating room workflows—while maintaining complete surgeon control at every step. The system continuously maps the surgical field and identifies key anatomical structures, while the robotic components translate the surgeon’s input into steady, highly controlled movements. This integration enhances both tissue detection and safety in the operating room.
The Polaris™’s development started at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), 15 years ago.
“The key challenges included designing a robotic arm capable of safely operating within the confined space of the eye, developing a visualization system that combines real-time digital microscopy with optical coherence tomography (OCT) and AI guidance, and fully integrating those systems into a cohesive, surgeon-centered platform. Each step of that process was shaped by collaboration between engineers and surgeons to ensure Polaris™ could fit naturally into existing surgical workflows while supporting precision and consistency,” Jean Pierre Hubschman, M.D., founder and CEO of Horizon Surgical Systems, told MedicalExpo e-Magazine.
Cataract surgery is the most frequently performed operation worldwide, with more than 5 million procedures taking place annually in the United States alone. While success rates are high, outcomes can vary based on surgeon technique, case complexity, and training level, factors that are increasingly challenging amid workforce shortages and rising patient demand. In the coming months, Horizon expects to treat additional patients and demonstrate the expanded capabilities of Polaris™. Additionally, Horizon believes that the Polaris™ has the potential to extend into minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) and retina surgery, areas where AI and robotics can address complexity, variability, and unmet needs.
“In 2026, we plan to gather insights from ongoing clinical studies to inform the next phase of system improvements, continue expanding our team, and advance Polaris™ toward Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval and commercialization,” says Jean Pierre.
Ion Endoluminal System (Intuitive Surgical)
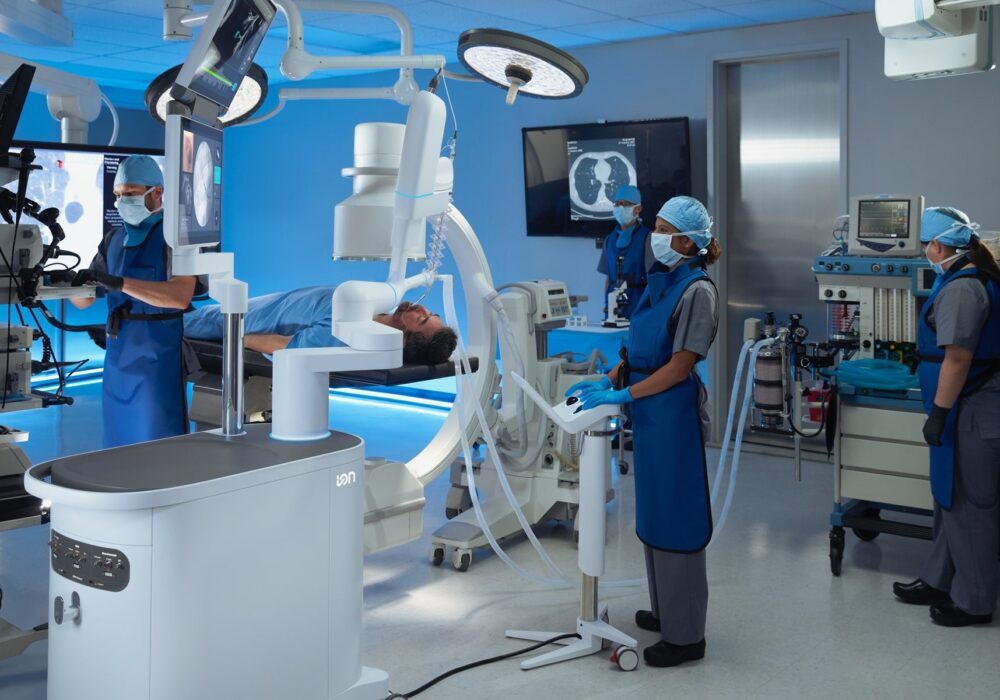
Another important announcement this October was Intuitive’s report that the FDA has cleared software advancements (AI integrated with expanded advanced imaging technologies) for Intuitive Surgical’s Ion Endoluminal System. Ion is a robotic-assisted bronchoscopy platform that features an ultra-thin, shape-sensing catheter designed to navigate deep into the lung. This advanced technology enables physicians to access small, hard-to-reach nodules and precisely position biopsy tools to sample potentially cancerous tissue. This new software update adds artificial intelligence to all of Ion’s navigation processes and includes new advanced imaging features to help make lung biopsies more accurate and efficient.
Lung cancer has been the leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally for over 25 years, and studies show that early diagnosis is associated with higher survival rates. As investigation often requires a biopsy of complex nodules in challenging locations within the lung, resources like the Ion can be crucial in lung cancer management. The key challenge addressed is known as CT-to-body divergence, which occurs when a lung nodule shifts to a different location during the procedure compared to its position in the pre-procedure CT scan due to lung movement, making it more difficult for doctors to accurately reach the target and perform an effective biopsy. Ion will now use AI to help correct the situation in real time. By combining computer vision with Ion’s shape-sensing technology, the system compares live images to the original plan and adjusts the view along the navigation path as needed—just like a rerouting GPS.
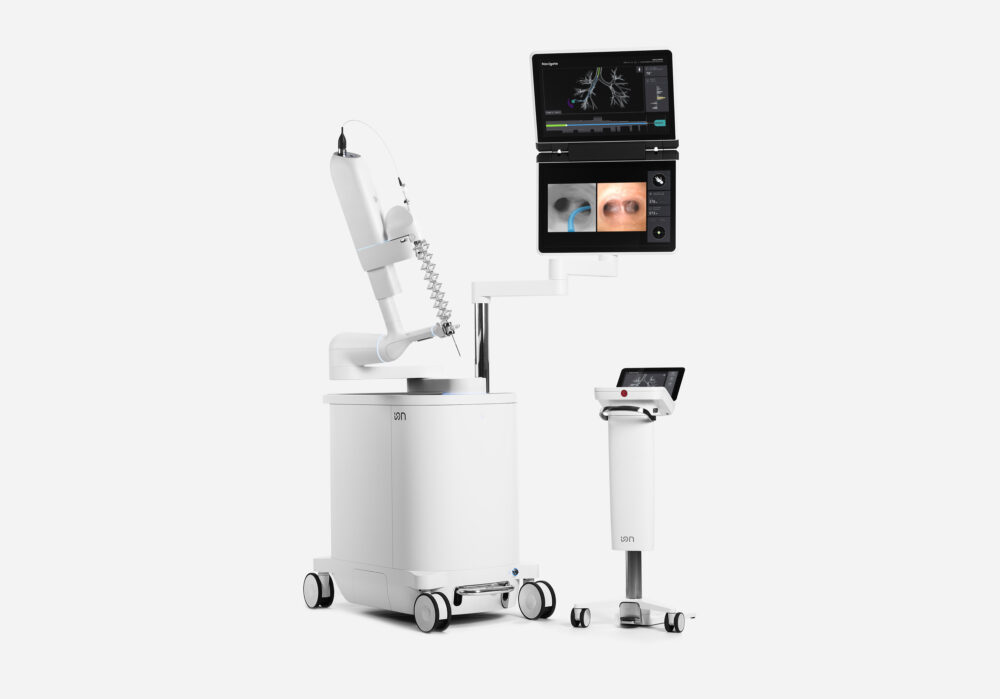

“Intuitive has been a leader in digital innovation for 30 years. We value data and the actionable insights it provides to help reduce variability and improve patient outcomes. With Ion’s fiber-optic shape sensor, the system gives precise information about the location, shape, and direction of the fiber to the doctor during the whole navigation and biopsy process. Such data is essential to performing accurate biopsies, as the desired position and orientation of the catheter is maintained by robotic assistance throughout the procedure,” a spokesperson of Intuitive Surgical told MedicalExpo e-Magazine.
Intuitive Surgical will initially introduce these software features through a limited launch, aiming to gather insights into performance across various clinical and operational environments. A broader launch in the United States is planned for 2026. As of June 30, 2025, there were more than 900 Ion systems in hospitals across 10 countries. In addition, the body of evidence continues to grow with more than 100 abstracts and publications describing the potential value it delivers to patients.
“Our vision for improving patient care leverages AI to deliver insights before, during, and after procedures. Today’s digital tools lay the foundation for surgeons to benefit as AI capabilities mature. Like any other technology, AI should be viewed through the value it brings in helping surgeons deliver more efficient, higher-quality clinical care,” the spokesperson adds.
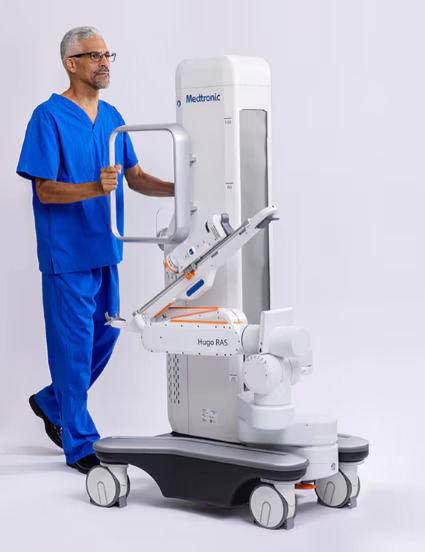
Hugo™ (Medtronic)
With 1.5 million procedures performed annually in the United States alone, hernia repair is one of the most common surgeries. These operations address conditions where part of the intestine bulges through weakened abdominal muscles. Left untreated, hernias can lead to pain, digestive troubles, swelling, or infection.
This finding highlights the significance of Medtronic’s announcement in September regarding the excellent results from the Enable Hernia Repair clinical study, which was a prospective, multi-center, single-arm pivotal study involving 193 patients and marked the first-ever Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) clinical study completed for robotic-assisted hernia surgery in the United States. The performance of its Hugo™ robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) system was evaluated in inguinal and ventral hernia repair procedures.
Key findings included a surgical success rate of 100%. Only two surgical site events (SSE) occurred among the 94 patients undergoing ventral hernia repair procedures, and these resolved without any complications.
Today, more than 30 countries across five continents clinically use the Hugo RAS system. In the European Union, the Hugo™ RAS system is CE marked. In the United States, the Hugo™ RAS system is an investigational device that is not for sale.