A new study by Benchling reveals that while large biopharma companies are rapidly adopting AI and automation to accelerate R&D, smaller firms face significant challenges in implementation due to costs, system fragmentation, and limited infrastructure.
A recent study by Benchling has revealed that artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming integral components of research and development (R&D) in the biopharmaceutical industry, particularly for large companies.
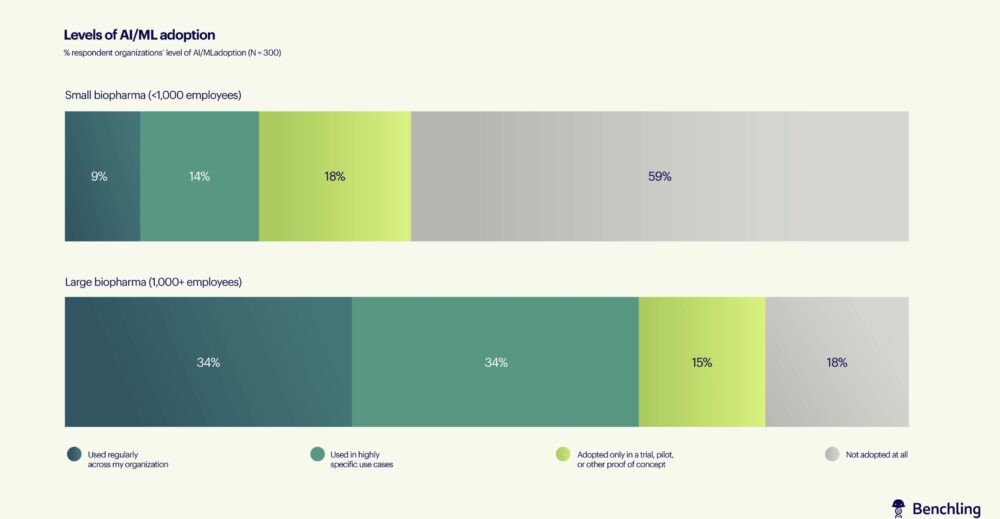
According to Benchling’s 2024 Biopharma Technology Landscape report, 75% of large biopharma companies use AI to accelerate R&D processes. Despite these advances, the report highlights a notable disparity in the adoption of AI between large enterprises and smaller firms, with only 28% of the latter incorporating these technologies.
Through AI, biopharma companies are automating the analysis of extensive datasets, identifying new therapeutic targets, and optimizing clinical trial designs. AI is seen as a key driver in reducing the time to market for new treatments. In fact, 75% of large biopharma companies anticipate that AI and ML will significantly speed up their R&D processes within the next 12 to 24 months. However, smaller companies remain cautious, often limited to pilot projects or exploratory use cases, which is reflected in their slower rate of adoption.
Data Platforms and Automation: Critical Tools in R&D Transformation
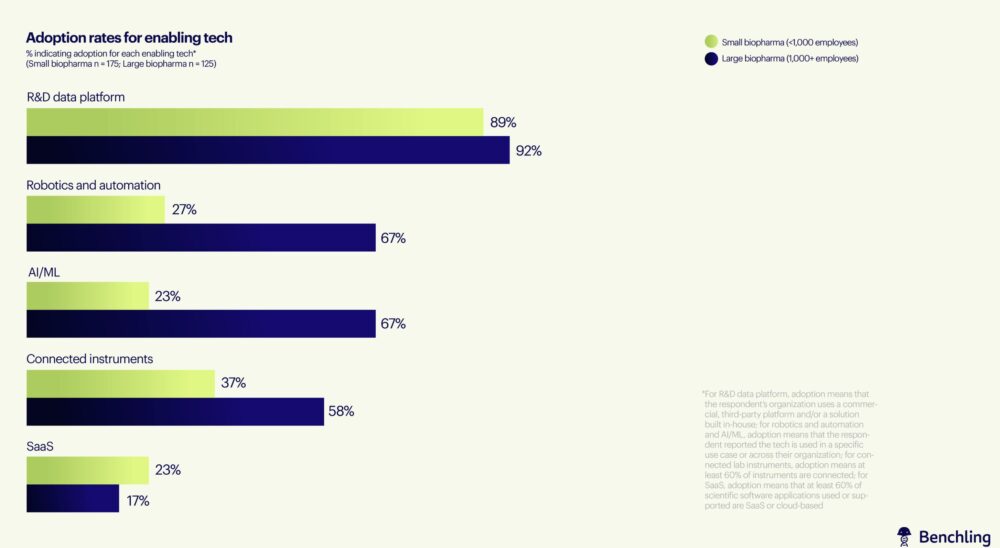
Automation and advanced data management platforms are also playing pivotal roles in the digital transformation of biopharma R&D. Large companies are adopting these technologies at a rapid pace, particularly in the areas of robotic automation and data platform integration. Benchling’s report found that large biopharma companies are twice as likely as smaller firms to use automation in their laboratories, a development that has enabled them to streamline their research workflows and increase overall productivity.
However, challenges remain. Connectivity between laboratory instruments and the adoption of cloud-based scientific software solutions are still limited. Only 23% of small biopharma companies and 17% of large ones have adopted cloud-based scientific software, which restricts their ability to fully exploit the potential of AI. Additionally, many laboratories—both large and small—struggle with automating data capture, with just 37% of small companies reporting that more than 60% of their laboratory instruments have automated data collection capabilities. This gap underscores the need for greater investment in digital infrastructure across the sector.
Persistent Barriers to Full AI Adoption
Despite the promising advancements in AI and automation, Benchling’s report identifies several obstacles that continue to hinder the full adoption of these technologies in the biopharma industry. Chief among them are the fragmentation of IT systems, high technology costs, limited connectivity, and a shortage of skilled talent. The report highlights that 54% of scientific software used by large biopharma companies is custom-built, making it difficult to integrate new technologies like AI and ML into existing workflows.
Moreover, the complexity of managing large-scale laboratory operations presents further challenges. According to the report, 36% of IT managers in large biopharma companies oversee more than 100 laboratory instruments, requiring enhanced interoperability between systems to ensure smooth operations. Regulatory concerns, data security, and the fragmented nature of IT systems also pose significant barriers, with 68% of large companies citing these factors as obstacles to adopting cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions. This fragmentation limits the seamless integration of AI technologies, hindering the overall efficiency of R&D operations.
Technological Divide Between Large and Small Companies
The report also highlights a growing technological divide between large and small biopharma companies when it comes to AI and automation. While large companies are making substantial investments in these areas, smaller firms are struggling to keep up due to the high costs of implementing automation and robotics. Benchling found that 78% of small companies view the cost of these technologies as a major barrier to adoption, limiting their ability to leverage AI-driven innovations that could enhance productivity and streamline R&D efforts.
Despite these challenges, improving productivity remains a key motivation for both large and small companies to adopt R&D data platforms. According to the report, 62% of large companies and 54% of small companies identified productivity gains as the primary driver for adopting these platforms. However, while 66% of smaller firms rely on commercial solutions to manage their R&D data platforms, 56% of large companies prefer hybrid solutions that combine commercial and custom-built systems. This divergence in approach underscores the different strategies employed by companies based on their size and resources.
Bridging the Gap: Toward a More Connected Biopharma Industry
As AI and digital technologies continue to reshape the biopharma landscape, the industry faces a critical challenge in bridging the technological gap between large and small companies. While large firms are rapidly advancing in their adoption of AI, automation, and data platforms, smaller companies remain hesitant, often limited by financial constraints and a lack of infrastructure. To fully capitalize on the opportunities presented by AI, the biopharma industry will need to address key challenges related to technology integration, data quality, and the adoption of cloud-based infrastructures.
The report emphasizes the importance of connectivity between wet and dry laboratories as a critical factor in achieving full AI readiness. Currently, only 41% of large companies report good integration between these two types of laboratories, a shortfall that could hinder their ability to fully leverage AI-driven insights in R&D. Addressing this gap, along with improving system interoperability and enhancing workforce expertise, will be essential steps toward realizing the full potential of AI in biopharma R&D.
Benchling’s 2024 Biopharma Technology Landscape report paints a clear picture of an industry in transition. While large biopharma companies are leading the charge in AI adoption, significant challenges remain in fully integrating these technologies into R&D workflows. For smaller companies, the cost of automation and the complexity of implementing AI solutions continue to be major obstacles. Nevertheless, the future of biopharma R&D appears increasingly digital, with AI, ML, and automation poised to play central roles in shaping the next generation of drug discovery and development.